Introduction
While designing new items or modifying structure of those already producing ones, a task of predicting their operational properties, particularly their service lifetime and energy efficiency, arises. These indexes are determined first of all by the characteristics of the friction units and their elements in the structure of the items such as wear resistance, friction coefficient, corrosion resistance. In order to get information about these performances quickly, the laboratory tests which are a part of the rational testing cycle (RTC) are held according to GOST 30480. In accordance with the mentioned GOST, ‘a compulsory stage of the rational testing cycle is revealing compatibility limits of a friction pair under laboratory conditions, assessing its friction-wear characteristics in relation to the operational modes of the friction unit under study, and detecting the critical points based on these tests’.
The Modengy company is the developer and producer of the anti-friction solid-film coatings. These coatings enable to create an ultrathin сomposite layer on the surface providing low low shear resistance of the contacting parts. In other words, we get a surface with already integrated lubricating material that provides life-time lubrication, and enables to create the friction unit that requires no maintenance.
In Bryansk town, the Modengy’s testing center operates, and its capabilities enable to predict operational properties of the friction units already on the stage of designing them. We help the industrial enterprises assess such important parameter as friction coefficient, wear intensity, frictional heating, anticorrosive properties. We are going to consider the test types in more details here below.
Corrosion tests
Tests for resistance to climatic factors are held according to GOST 30630.2.5 (ISO 9227). They are performed in the automatic salt mist chambers. The given method enables to identify anticorrosive properties of the coatings, corrosion resistance of the constructive materials, and the items made of them. Since this method is widely used in international practice, and is included into many specifications, the results of these tests can be assessed in comparative aspect.
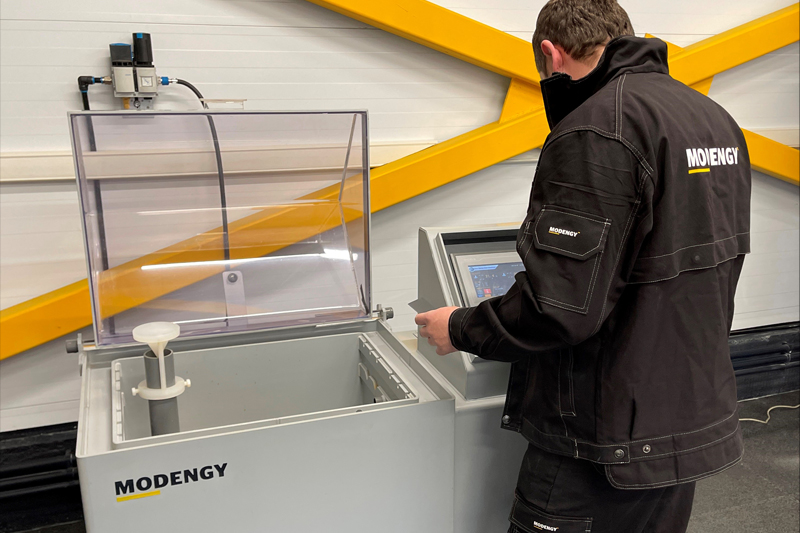

Fig.1. Tests for salt mist exposure
Friction and wear tests
The laboratory tribotechnical tests are held on the diminutive samples by using various friction schemes (see Fig. 2). In the USSR, the roller friction machines implementing the ‘pad-roller’ scheme were mostly spread (see Fig.2a). Nowadays, the schemes with a focused contact such as the ‘sphere- plane’ one at rotating or back-and-forth motion are the most frequently used for comparative tests (see Fig. 2с). Using them enables to eliminate the sample and counter-body putting error, to cut down the running-in period on macro-level, to make testing time shorter, and to get the results faster.
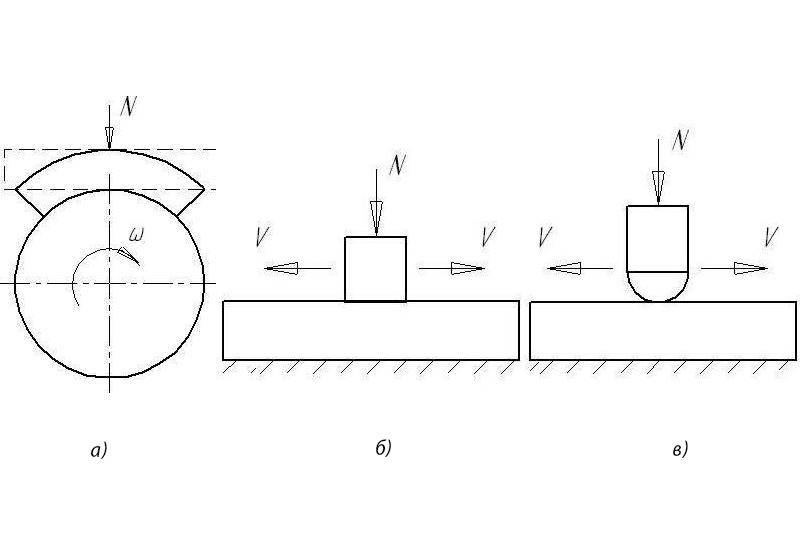
Fig.2. Friction scheme at testings
At the Modengy’s testing center, friction and wear tests are held using every of the mentioned friction schemes including the schemes presented on Fig. 2b and 2c according to ASTM G99 and ASTM G133 standards. The test machines are developed with participation of the leading experts in the field of tribology of the Theoretical Engineering Institute of the Russian Science Academy named after A.Blagonravov. General view of the test plant for testing according to ASTM G99 and its load block is presented on Fig.3 and Fig.4.
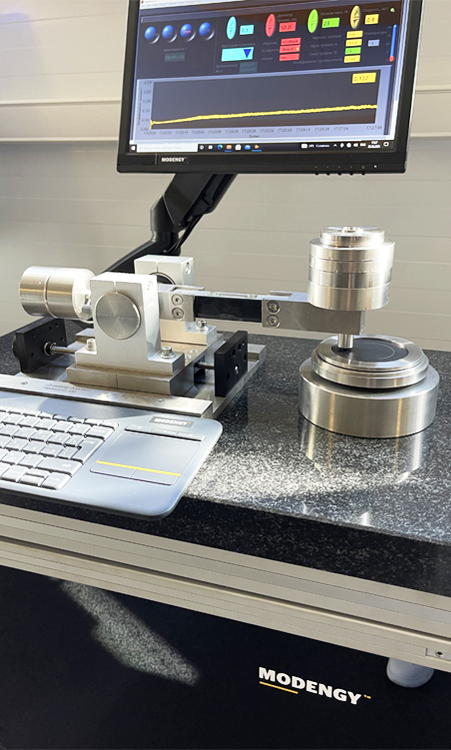

Fig.3. Process of installing the test plant in the laboratory
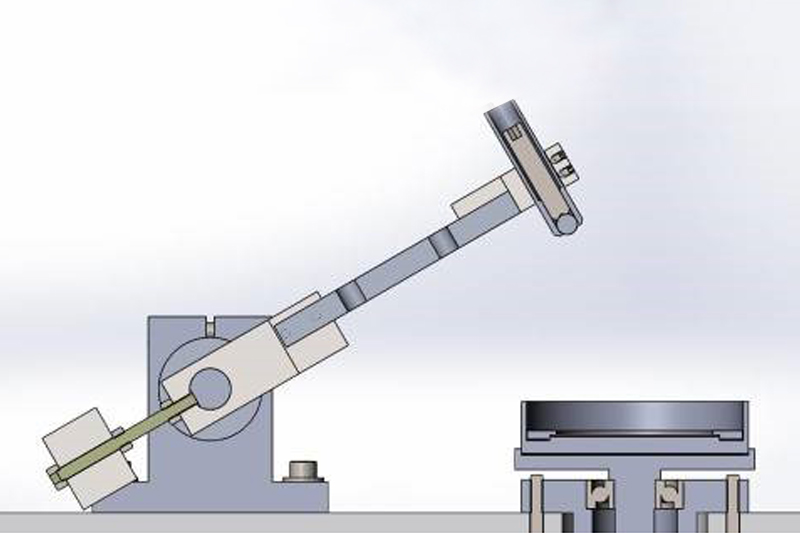
Fig.4. The load block of the test plant
An example of the test results is presented on Fig.5. As soon as dependence values of friction coefficient and wear resistance on slide rate, contact pressure, and operation environment nature are gained, it is possible to identify the optimal operation modes, and critical points for the pair under study, and detect their application limits. In process of testing it is also possible to explore the friction temperature mode in the form of taking temperature fields readings (see Fig.6).
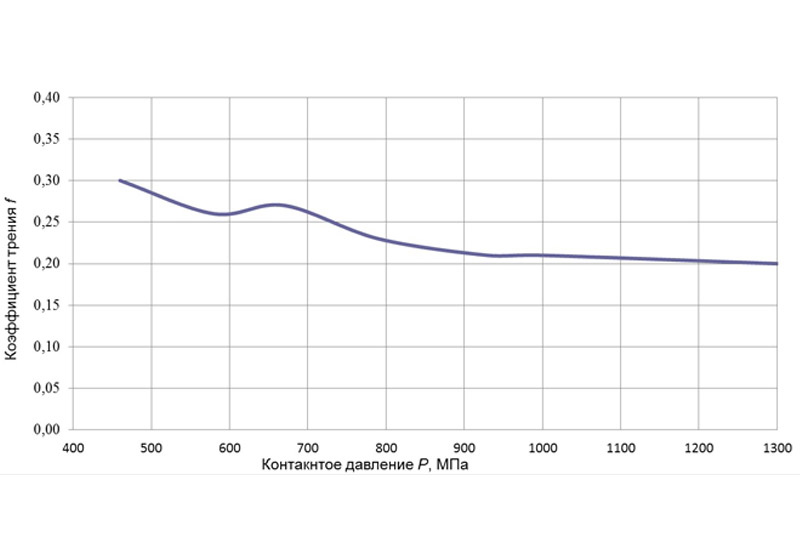
Fig.5. An example of test results in the form of friction coefficient dependence (f) on contact pressure (P)

Fig.6. Studying temperature fields of a friction pair
Microstructural studies
These studies are held to assess the structure of the coating in its initial state, and then after the tribotechnical tests as well as uniformity of coating distribution over the surfaces of complicated shapes. The samples for studying MODENGY 1014 coating on the internal threaded surfaces of the pump-compressor pipe coupling are presented on Fig.7, and the resulting photo that gives an opportunity to assess uniformity of the coating, and any defects presence is on Fig.8. The microstructural studies enable to work through the coating applying technology to provide their best quality on the surfaces of a complicated geometry, and with high requirements towards accuracy.
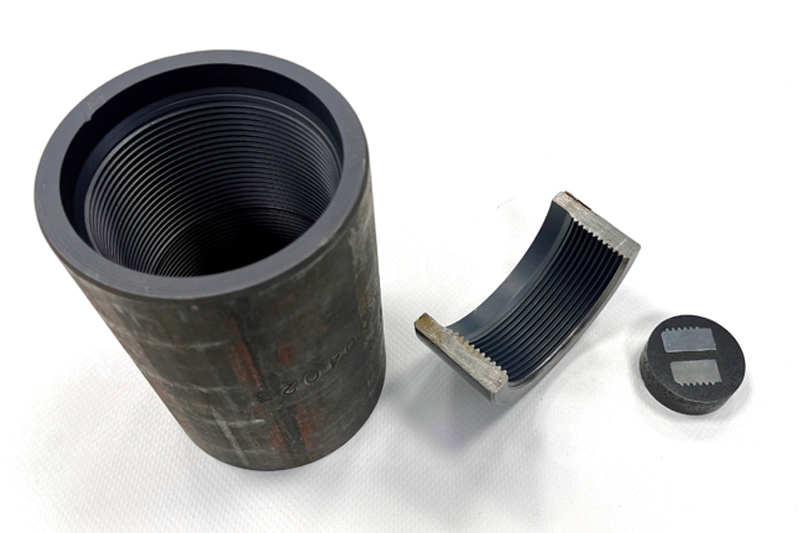

Fig.7. Samples for microstructual studies
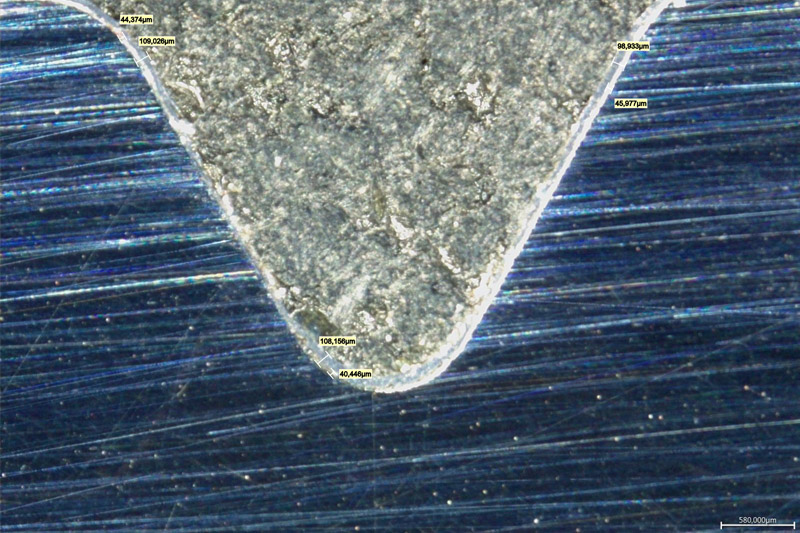
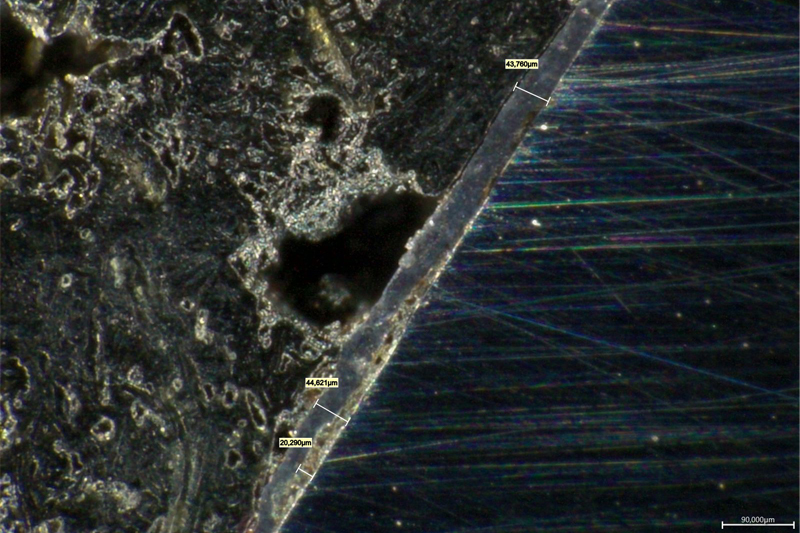
Fig.8. A micro-photo of the internal threaded surface section of the pump-compressor pipe coupling coated with MODENGY 1014
Conclusion
Holding the laboratory tests on the stage of designing an item enables to select the optimal materials and coatings for the friction pairs taking into account the application limits, to predict service lifetime, and to assess other operational properties. The experts of the Modengy’s testing center while analyzing this or that friction pair consider it first of all as a system with multiple elements and external impacts. By using the system approach, it gets possible to achieve the required output parameters such as friction coefficient and wear intensity by changing certain system elements in a wanted direction.
For more detailed information, and to get a consultation, please contact our experts.
Request information




 RU
RU
 EN
EN




